| Method | Checks that | New in |
| assertEqual(a, b) | a == b |
|
| assertNotEqual(a, b) | a != b |
|
| assertTrue(x) | bool(x) is True |
|
| assertFalse(x) | bool(x) is False |
|
| assertIs(a, b) | a is b |
2.7 |
| assertIsNot(a, b) | a is not b |
2.7 |
| assertIsNone(x) | x is None |
2.7 |
| assertIsNotNone(x) | x is not None |
2.7 |
| assertIn(a, b) | a in b |
2.7 |
| assertNotIn(a, b) | a not in b |
2.7 |
| assertIsInstance(a, b) | isinstance(a, b) |
2.7 |
| assertNotIsInstance(a, b) | not isinstance(a, b) |
2.7 |
如果我们在 factorial.py 中调用 div(0),我们能看到异常被抛出。
我们也能测试这些异常,就像这样:
self.assertRaises(ZeroDivisionError, div, 0)
完整代码:
import unittest
from factorial import fact, div
class TestFactorial(unittest.TestCase):
"""
我们的基本测试类
"""
def test_fact(self):
"""
实际测试
任何以 `test_` 开头的方法都被视作测试用例
"""
res = fact(5)
self.assertEqual(res, 120)
def test_error(self):
"""
测试由运行时错误引发的异常
"""
self.assertRaises(ZeroDivisionError, div, 0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
mounttab.py 中只有一个 mount_details() 函数,函数分析并打印挂载详细信息。
import os
def mount_details():
"""
打印挂载详细信息
"""
if os.path.exists('/proc/mounts'):
fd = open('/proc/mounts')
for line in fd:
line = line.strip()
words = line.split()
print('{} on {} type {}'.format(words[0],words[1],words[2]), end=' ')
if len(words) > 5:
print('({})'.format(' '.join(words[3:-2])))
else:
print()
fd.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
mount_details()
重构 mounttab.py
现在我们在 mounttab2.py 中重构了上面的代码并且有一个我们能容易的测试的新函数 parse_mounts()。
import os
def parse_mounts():
"""
分析 /proc/mounts 并 返回元祖的列表
"""
result = []
if os.path.exists('/proc/mounts'):
fd = open('/proc/mounts')
for line in fd:
line = line.strip()
words = line.split()
if len(words) > 5:
res = (words[0],words[1],words[2],'({})'.format(' '.join(words[3:-2])))
else:
res = (words[0],words[1],words[2])
result.append(res)
fd.close()
return result
def mount_details():
"""
打印挂载详细信息
"""
result = parse_mounts()
for line in result:
if len(line) == 4:
print('{} on {} type {} {}'.format(*line))
else:
print('{} on {} type {}'.format(*line))
if __name__ == '__main__':
mount_details()
同样我们测试代码,编写 mounttest.py 文件:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import unittest
from mounttab2 import parse_mounts
class TestMount(unittest.TestCase):
"""
我们的基本测试类
"""
def test_parsemount(self):
"""
实际测试
任何以 `test_` 开头的方法都被视作测试用例
"""
result = parse_mounts()
self.assertIsInstance(result, list)
self.assertIsInstance(result[0], tuple)
def test_rootext4(self):
"""
测试找出根文件系统
"""
result = parse_mounts()
for line in result:
if line[1] == '/' and line[2] != 'rootfs':
self.assertEqual(line[2], 'ext4')
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
运行程序
$ python3 mounttest.py
..
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 2 tests in 0.001s
OK
测试覆盖率是找到代码库未经测试的部分的简单方法。它并不会告诉你的测试好不好。
在 Python 中我们已经有了一个不错的覆盖率工具来帮助我们。你可以在实验楼环境中安装它:
$ sudo pip3 install coverage
覆盖率示例
$ coverage3 run mounttest.py
..
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 2 tests in 0.013s
OK
$ coverage3 report -m
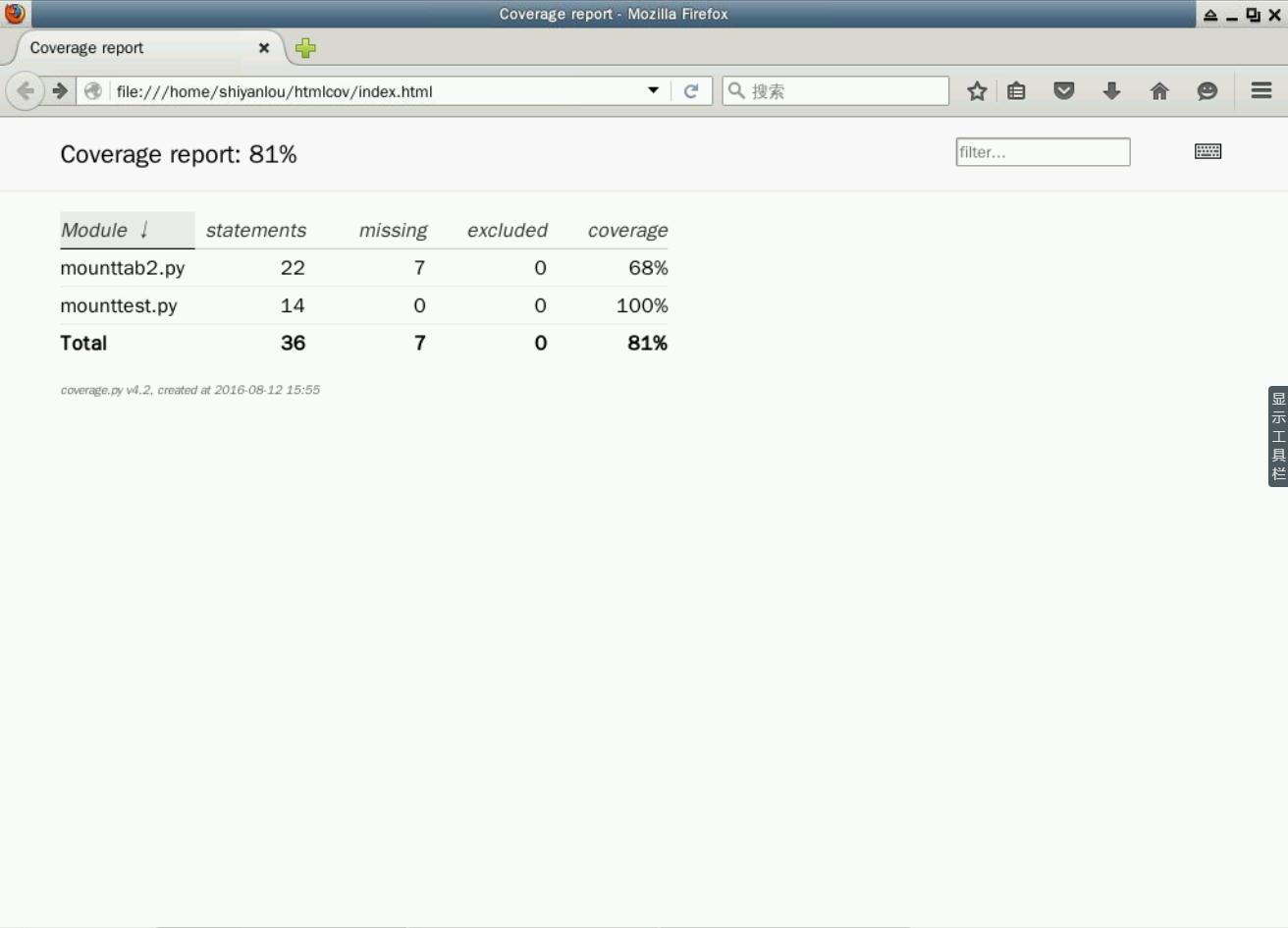
Name Stmts Miss Cover Missing
--------------------------------------------
mounttab2.py 22 7 68% 16, 25-30, 34
mounttest.py 14 0 100%
--------------------------------------------
TOTAL 36 7 81%
我们还可以使用下面的命令以 HTML 文件的形式输出覆盖率结果,然后在浏览器中查看它。
$ coverage3 html
知识点回顾:
本节了解了什么是单元测试,unittest 模块怎么用,测试用例怎么写。以及最后我们使用第三方模块 coverage 进行了覆盖率测试。
在实际生产环境中,测试环节是非常重要的的一环,即便志不在测试工程师,但以后的趋势就是 DevOps,所以掌握良好的测试技能也是很有用的。
到此这篇关于浅谈如何测试Python代码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关测试Python代码内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!